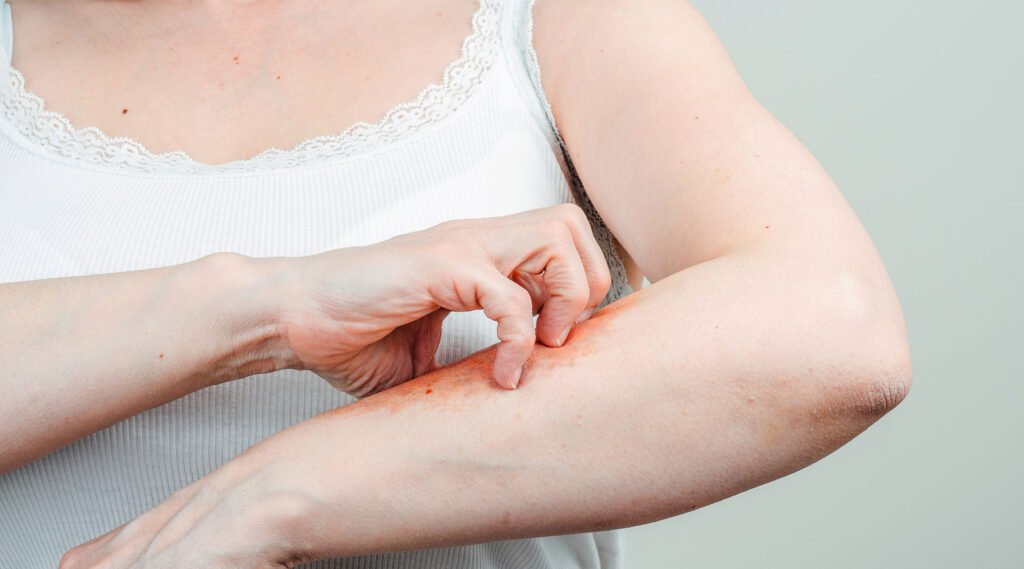
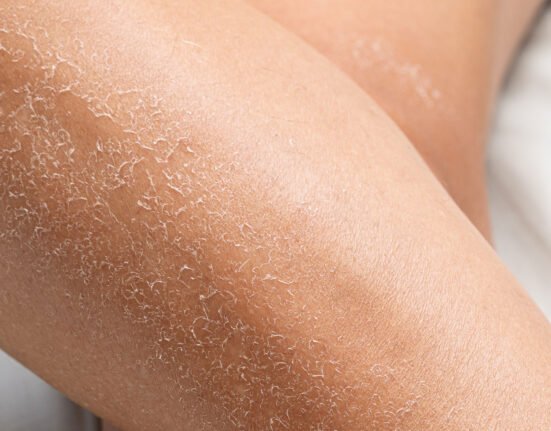
Dark scars are one of the most common concerns after the skin experiences abrasions or minor injuries.
These darker marks often appear as part of the body’s natural healing process. However, they can cause the skin to look uneven and affect its appearance.
When a scar forms, it is actually the body’s way of repairing damaged skin. Any wound—whether a cut, scrape, burn, or abrasion—triggers the body to produce scar tissue, which is mostly made of collagen.
This tissue allows the skin to close and heal properly.
However, the development of dark scars can vary widely. Many factors affect the final result, including the level of inflammation, the size and depth of the wound, its location, skin condition, and how the wound is cared for from the beginning.
This is why no two scars are ever the same—each person has a unique healing pattern.
In the early stages, scars are usually red or pink and may feel sore. Over time, their color will change as healing progresses.
Some scars look thick and reddish, while others become thinner and lighter.
In some cases, scars can become darker or even black. This is known as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, which commonly affects individuals with medium to darker skin tones.
So, what exactly causes dark scars to appear after a skin abrasion?
Causes of Dark Scarring After Wound Healing
Dark scars that appear after a wound heals are influenced by the skin’s healing process and melanin production.
Melanin is the natural pigment that determines our skin color, produced by specialized cells known as melanocytes. These cells protect the skin from sun exposure.
However, when the skin is injured, the healing process can affect how melanocytes function. In deeper wounds—such as burns, cuts, or acne—the inflammation can damage or even destroy the pigment-producing cells.
As a result, melanin production becomes unstable.
This condition can lead to dark marks (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation), especially when:
- There is significant inflammation
- The skin is exposed to sunlight during healing
- The wound is poorly treated, prolonging the recovery process
- Genetics play a role, particularly in individuals with darker skin who naturally produce more melanin
The combination of these factors causes the scarred area to appear darker than the surrounding skin.
Skincare Ingredients That Help Fade Dark Marks
To help fade dark scars, certain skincare ingredients can effectively inhibit melanin production, speed up skin regeneration, and even out skin tone. Commonly recommended topical agents include:
1. Hydroquinone
A skin-lightening agent that works by inhibiting melanin-producing enzymes. It is effective for stubborn hyperpigmentation, but should be used under medical supervision as it may irritate when misused.
2. Kojic Acid
Derived from fungal fermentation, kojic acid helps reduce dark spots by slowing pigment formation. It is suitable for routine use as it is generally gentler than hydroquinone.
3. Glycolic Acid
An AHA that exfoliates dead skin cells and stimulates new cell turnover. With regular use, dark scars can appear brighter, and the skin becomes smoother.
4. Tretinoin
A vitamin A derivative that accelerates skin cell renewal, making it effective for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Tretinoin also stimulates collagen production, helping improve the texture of scarred skin.
These ingredients can help fade dark scars when used correctly and consistently. However, because some of them are quite potent, it is important to monitor for irritation and always use sunscreen for optimal results.
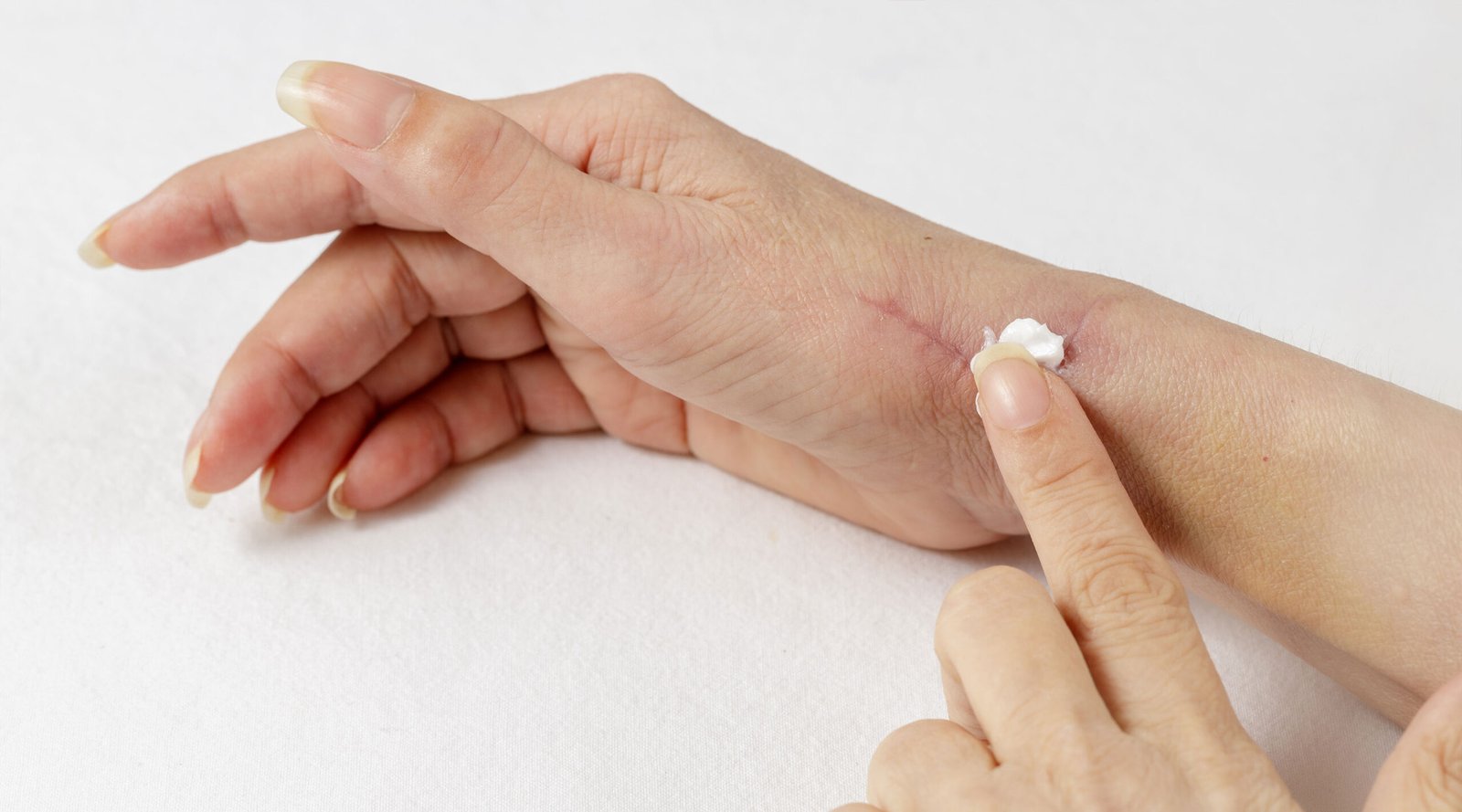
Daily Care Tips to Prevent Scars From Darkening

Proper wound care from the beginning is essential to prevent persistent dark scars. Here are care steps that can help keep the skin bright and minimize discoloration:
1. Keep the wound clean
Clean the wound with mild soap and running water. Avoid harsh products such as hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, iodine, or antibacterial soaps.
These can damage healthy skin cells, slow healing, and increase the risk of hyperpigmentation.
2. Moisturize regularly
Use a fragrance-free moisturizer or silicone gel to keep the wound area hydrated. Well-moisturized skin is more elastic and heals faster, reducing the likelihood of dark scars.
3. Limit sun exposure
UV rays are major triggers of hyperpigmentation. Apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher when the scarred area is exposed to the sun.
If possible, cover it with protective clothing to prevent further darkening.
4. Avoid picking scabs
Picking or scratching scabs can worsen inflammation, leave dark marks, and increase the risk of permanent scarring.
Allow scabs to fall off naturally.
5. Stay hydrated
Drinking enough water helps maintain a strong skin barrier. When the body is well-hydrated, the skin regenerates more efficiently and is less likely to develop dark marks.
6. Maintain a healthy diet
Consume foods rich in protein, healthy fats, zinc, selenium, and vitamins A, C, and E. These nutrients support tissue repair and help prevent post-injury hyperpigmentation.
7. Use silicone gel
Studies show that silicone gel effectively reduces the risk of hypertrophic scars and keloids.
It also helps minimize pigmentation, preventing darkening of the scar.
Start the right care routine today to help fade dark scars and restore a more even skin tone!
References
Cleveland Clinic. Accessed in 2025. Scars.
SPRSI. Accessed in 2025. Understanding Scar Discoloration.
Vibrant Dermatology. Accessed in 2025. What Causes Scars to Turn Dark?








Leave feedback about this