Post-wound care is essential to ensure that the skin heals properly without leaving scars or causing irritation.
Wounds heal gradually; the smaller the wound, the faster the recovery. Conversely, large or deep wounds usually take longer to heal.
When we experience cuts, scrapes, or punctures, the blood begins to clot within minutes to stop the bleeding.
This blood clot then dries and forms a scab, which protects the underlying tissue from germs and external dirt.
Not all wounds bleed, for example, burns, small puncture wounds, or pressure sores (decubitus ulcers).
However, regardless of the type, proper post-wound care is needed to ensure optimal healing and to prevent complications such as infection or scars that are difficult to remove.
In a healthy body, most wounds can heal on their own. However, several conditions can hinder wound healing, such as diabetes, anemia, vascular disorders, infections, advanced age, or unhealthy habits like smoking.
Natural Stages of Post-Wound Healing
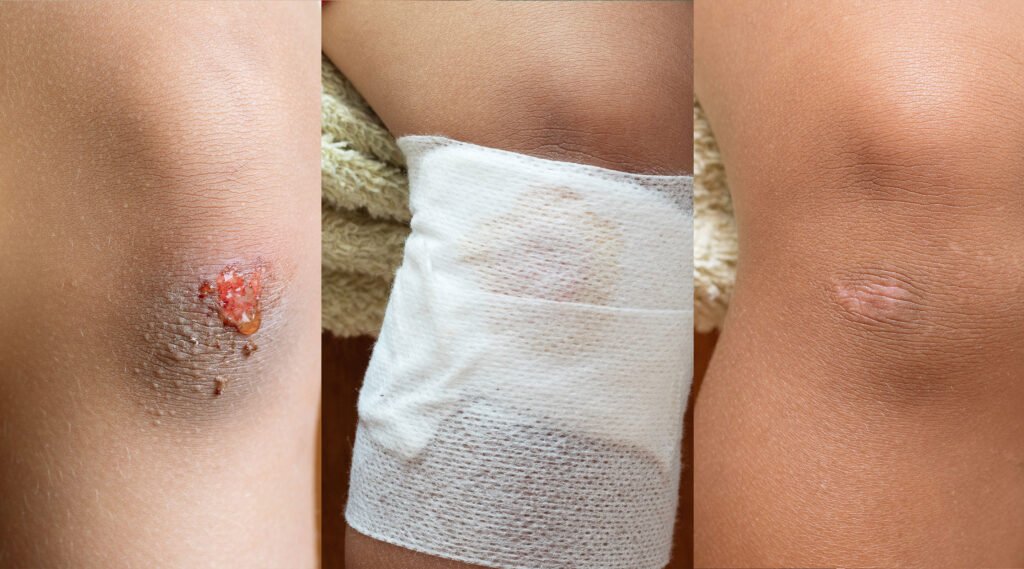
In the wound-healing process, it’s important to understand that natural skin recovery occurs through four main stages: hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling.
- Hemostasis: Stops bleeding by forming a protective scab.
- Inflammation: The body sends immune cells to clean the wound of germs and dead tissue. During this stage, the skin may appear red, swollen, warm, or tender.
- Proliferation: The body begins to form new tissue containing collagen and blood vessels to close the wound.
- Remodeling: The new tissue strengthens and starts to form scar tissue.
These stages can take weeks to months, depending on the size and type of wound. Therefore, proper post-wound care can speed up this natural process and reduce the risk of permanent scarring.
Post-Wound Care and Irritation Prevention
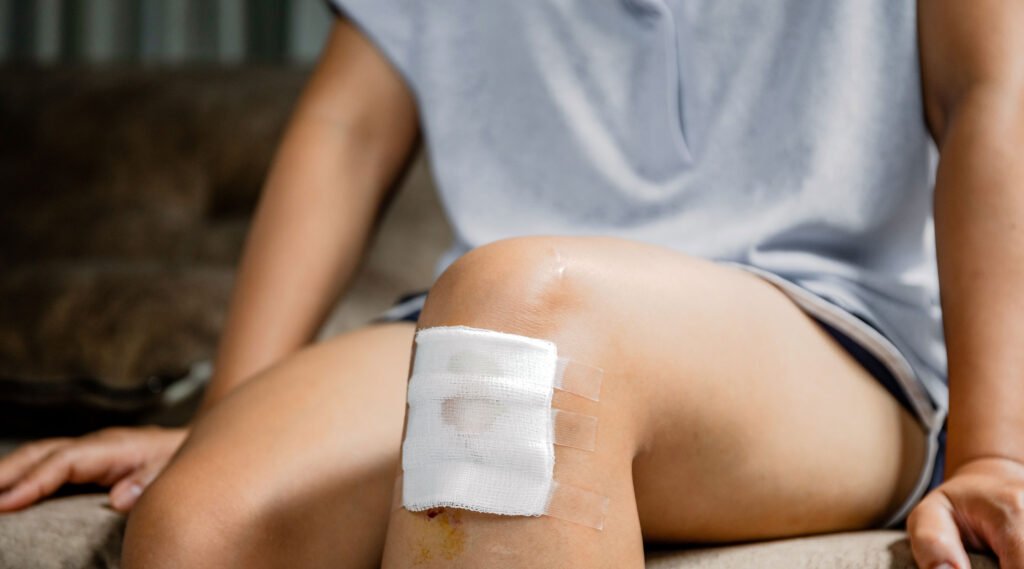
Scars often form because wounds are not properly treated from the beginning. With the right post-wound care, you can help the skin heal faster and minimize scarring.
Here are some important steps you can take at home:
1. Keep the wound clean
Gently clean the wound with mild soap and running water. Cleanliness is key to preventing germs from entering and worsening the wound condition.
2. Keep the wound moist
Apply petroleum jelly or a specialized wound-healing ointment to maintain skin moisture. Moist wounds tend to heal faster and are less likely to form thick scabs.
3. Cover the wound with a bandage
After cleaning and moisturizing, cover the wound with a sterile bandage. For larger wounds, use silicone sheets or hydrogel dressings to help reduce the risk of scarring.
4. Change bandages daily
Regularly changing bandages helps maintain wound hygiene and prevent infection. If your skin is sensitive to adhesive tape, opt for non-stick gauze or paper tape that is gentler on the skin.
5. Protect with sunscreen
Once the wound has closed, apply sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher to prevent discoloration on the scar caused by sun exposure.
Recommended Products for Post-Wound Care
Use gentle, safe, and effective skincare products to support skin regeneration. Products like wund+™ Regeneration Cream and wund+™ Wound Spray help maintain moisture, accelerate skin cell regeneration, and protect the wound area from infection risk.
With proper post-wound care, your skin will not only heal faster but also stay free from irritation and unsightly scars.
References
Better Health. Accessed in 2025. Wounds – how to care for them
Medline Plus. Accessed in 2025. How Wounds Heal.
MDPI. Accessed in 2025. Wound Healing Properties of Natural Products: Mechanisms of Action







Leave feedback about this