Everyone experiences wounds at some point, from minor scrapes to more serious injuries. But did you know that not all wounds heal in the same way or within the same timeframe?
Based on recovery duration, wounds are generally divided into two categories: acute wounds vs chronic wounds.
Understanding the difference is important to ensure proper treatment and prevent complications.
Recognizing the distinctions between acute wounds and chronic wounds can significantly impact treatment strategies.
What Is an Acute Wound?
An acute wound occurs suddenly, usually due to trauma—such as burns, cuts, punctures, or surgical incisions.
Typically, acute wounds heal within 1–4 weeks if treated properly. The healing process is relatively quick and rarely causes serious problems.
However, there are warning signs to watch out for. Acute wounds may become more serious if you notice severe swelling, increasing pain, fever, pus or excessive inflammation
If these occur, an acute wound may develop into a chronic wound.
What Is a Chronic Wound?
A chronic wound fails to heal within the normal timeframe. Generally, a wound is considered chronic if it shows no improvement after 4 weeks or hasn’t fully healed after more than two months, despite care.
Chronic wounds often remain stuck in the inflammation stage, which slows recovery. Common causes include:
- Untreated infection
- Improper wound care
- Underlying medical conditions, such as:
- Diabetic wounds (e.g., diabetic foot ulcers)
- Pressure ulcers (bedsores) in patients confined to bed or a wheelchair
- Vascular wounds caused by poor blood circulation
- Traumatic wounds with inadequate care
How Wounds Impact Health
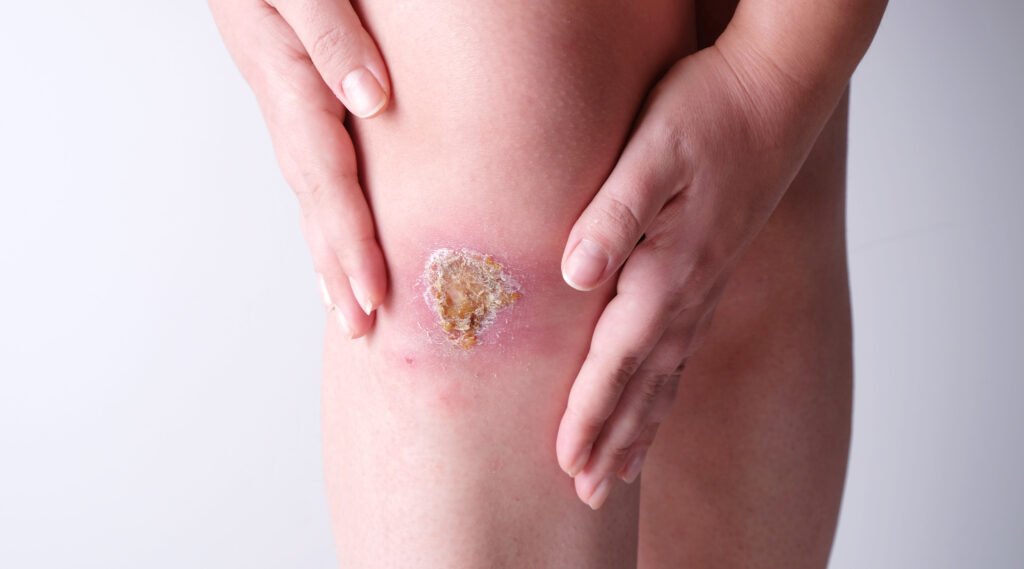
Beyond disrupting daily activities, wounds can lead to serious health issues, including:
- Risk of infection spreading deeper into tissues
- Persistent pain
- Reduced quality of life (limited mobility, discomfort, and even psychological effects)
- In severe cases, dangerous complications if not managed properly
How to Treat Acute Wounds vs. Chronic Wounds
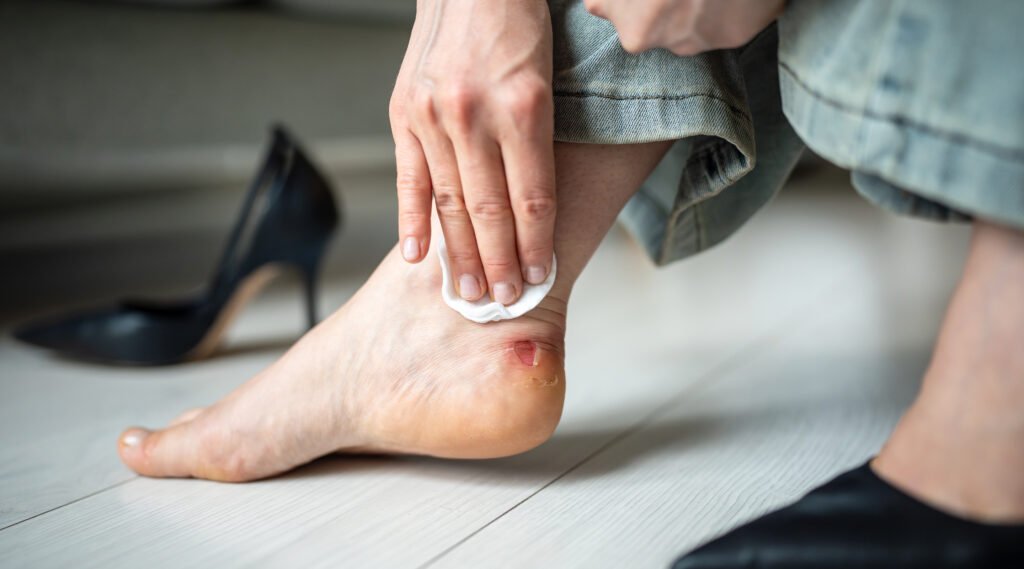
Acute Wound Care
- Gently clean the wound with clean water or a mild antiseptic
- Cover with a sterile dressing if necessary
- Change dressings regularly
- Seek medical help if the wound is deep, wide, or bleeding heavily
Chronic Wound Care
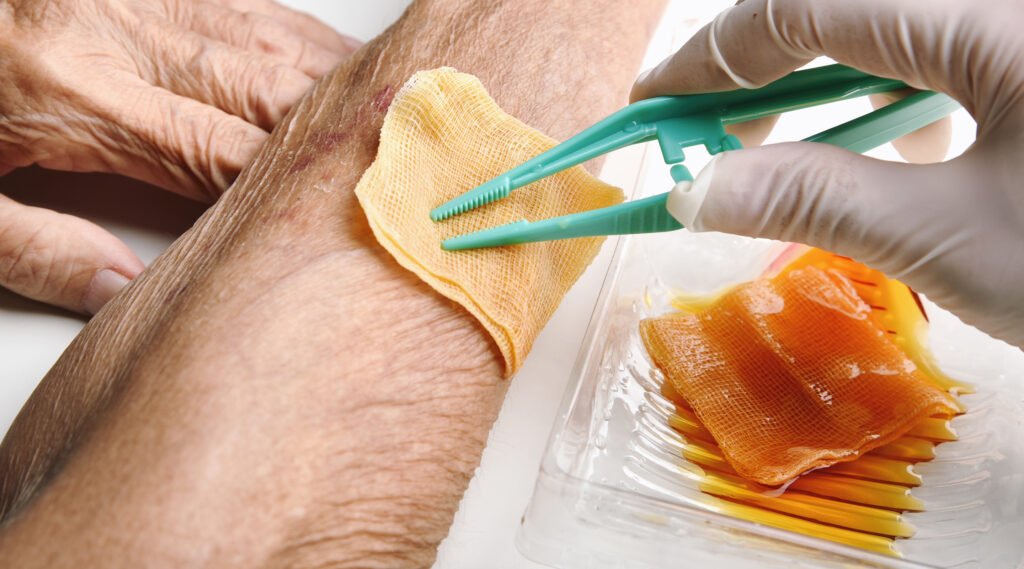
Treatment is more complex and requires professional medical attention. Common steps include:
- Routine cleaning to prevent infection
- Use of specialized dressings designed to support tissue regeneration
- Debridement (removal of dead tissue) by a doctor or nurse to optimize healing
- Nutritional support, ensuring adequate protein, vitamins, and minerals to aid skin regeneration
- Close monitoring, especially for patients with underlying conditions like diabetes
Acute wounds usually heal quickly, while chronic wounds take longer and need more intensive care.
Recognizing the difference early allows you to take the right steps. If a wound doesn’t heal as expected, consult a healthcare professional promptly to prevent serious complications.
References
Bangkok Hospital. Accessed in 2025. A comprehensive care for chronic wounds.
Byram Healthcare. Accessed in 2025. The Difference Between Acute and Chronic Wound Care








Leave feedback about this