Wounds can happen at any time. Proper wound care is essential to prevent infection, speed up healing, and minimize scarring.
An open wound refers to an injury that breaks the skin, either externally or internally.
These wounds are typically caused by accidents involving sharp or rough objects that cut the skin and cause trauma.
If left untreated, open wounds can expose the body to harmful bacteria and increase the risk of infection.
Just like other injuries, open wounds are classified into different types. While minor wounds can be treated at home, more severe injuries require emergency medical attention.
Being able to identify the type of wound can help you provide proper first aid when someone you care about is injured.
By understanding the different types of wounds, you can choose the right care and promote faster recovery.
Common Types of Wounds at Home
Abrasion
This occurs when the skin scrapes against a rough surface. Abrasions are usually shallow, with little or no bleeding. However, the area must be cleaned, as it may be contaminated with dirt or bacteria.
Incision
An incision is a clean, straight cut caused by sharp objects like knives, glass, or razors. If a tendon is involved, bleeding may be severe and could lead to permanent damage.
Treatment includes thoroughly cleaning the wound and, if needed, stitching.
Common examples at home include kitchen knife or razor blade cuts.
Puncture
Small but deep wounds caused by objects like needles or nails. These wounds may seem minor, but can be dangerous if contaminated.
In some cases, antibiotics or a tetanus shot may be required. Deep puncture wounds, such as gunshot wounds, need immediate medical attention.
Contusion (Bruise)
Caused by blunt force trauma that damages blood vessels under the skin without breaking the skin itself, for example, hitting your shin on a table leg.
Minor Burns
Usually caused by hot water, oil, or contact with a hot iron.
Home Wound Care
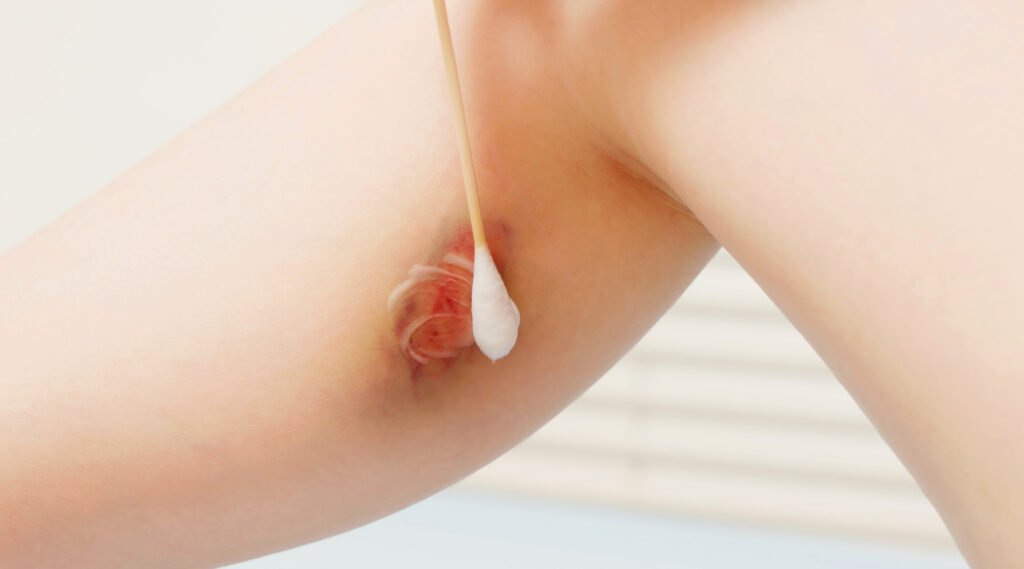
1. Wash your hands before touching the wound to prevent infection.
2. Clean the wound with clean water or a sterile solution such as wund+™ Wound Spray, which contains hypochlorous acid (HOCl) to cleanse and hydrate the wound.
3. Stop the bleeding by applying pressure with a clean cloth or sterile gauze.
4. Apply wund+™ Regeneration Cream to soothe the skin and support tissue regeneration (only on closed wounds).
5. Cover the wound with a sterile dressing appropriate for the wound size, such as a bandage or gauze.
6. Change the dressing regularly, especially if it becomes dirty or wet.
How to Care for Each Type of Wound
- Abrasion: Clean with wund+™ Wound Spray and pat dry gently.
- Incision: Stop bleeding with a clean cloth, then spray with wund+™ Wound Spray to prevent infection and support healing.
- Puncture: Due to the higher risk, clean immediately with an antiseptic solution, cover the wound, and monitor closely. Seek medical care if the wound is deep or dirty.
- Contusion: Apply a cold compress to reduce swelling. If the skin isn’t broken, a bandage isn’t necessary.
- Minor Burn: Cool the area under running water for 10–15 minutes, then apply wund+™ Regeneration Cream to soothe the skin. Avoid using toothpaste or butter, as they can worsen the burn.
Wound Care Products to Keep at Home
In addition to bandages, plasters, and sterile gauze, make sure your family first-aid kit includes:
- wund+™ Wound Spray: Quickly and gently cleanses wounds.
- wund+™ Regeneration Cream: Promotes faster skin regeneration and reduces the risk of scarring.
- wund+™ Scar Gel: For post-healing care to fade scars and restore smooth skin.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help if the wound:
- Is deep, large, or continues to bleed despite pressure
- Is it on the face or other sensitive areas
- Shows signs of infection: swelling, severe pain, pus, foul odor, or fever
- It is caused by animal bites or rusty objects, which increase the risk of tetanus
Caring for a wound at home isn’t just about covering it up. It’s about keeping it clean, moist, and protected from infection.
With proper treatment using products like wund+™ Wound Spray and wund+™ Regeneration Cream, wounds can heal faster and with fewer complications.
Don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional if the wound doesn’t improve.
References
Healthline. Accessed in 2025. Open Wound.
Makatimed. Accessed in 2025. Different Types of Open Wounds and How to Treat Them.








Leave feedback about this