Dehydrated skin? Yes, just as the body can become dehydrated, the skin can too. About 55–65% of the human body is water.
Almost all processes in the body—from cellular activity to the function of tissues and organs—require water to work correctly. The skin is no exception.
Every day, the body continuously loses fluids through sweating, urine, and breathing. Therefore, lost fluids need to be replenished regularly.
When fluid loss exceeds intake, dehydration can occur, affecting the entire body, including the skin.
Dehydrated Skin Is Different from Dry Skin
Dehydrated skin and dry skin are often mistaken for the same condition, even though they are different.
- Dehydrated skin is a temporary condition caused by a lack of water in the skin layers.
- Dry skin is a persistent skin type, often associated with a deficiency of natural oils (sebum).
Interestingly, dehydrated skin can occur even in oily skin types, as the main issue is not oil deficiency but a lack of water.
Dehydrated Skin Can Recover

The good news is that dehydrated skin can be rehydrated with simple lifestyle changes.
Some steps that can help include:
- Drinking at least 8 glasses of water per day, adjusted to body weight and activity level
- Consuming fruits and foods with high water content
- Maintaining a balanced fluid intake, as excessive water consumption can also disrupt the body’s mineral balance
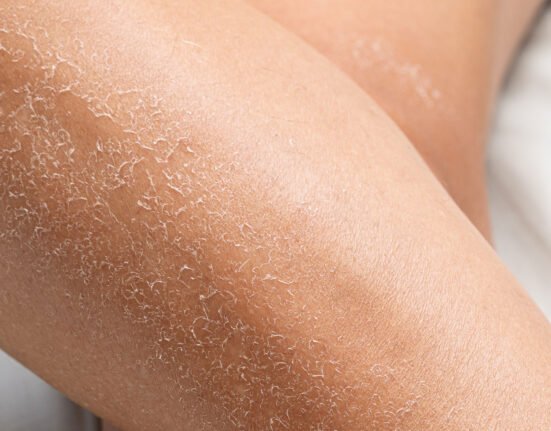
Signs of Dehydrated Skin
Mild dehydration is quite common, and one of the earliest signs often appears on the skin. Common signs of dehydrated skin include:
- Dry patches on the skin
- Rough, scaly, or itchy texture
- Fine lines are becoming more visible
- Dull-looking skin
- Reduced skin elasticity or firmness
If left untreated, dehydrated skin can become more sensitive and prone to irritation.
Causes of Dehydrated Skin
Skin dehydration occurs when the body and skin lose more fluids than they take in. Some common and often overlooked causes include:
- Not drinking enough water, especially during busy activities
- Excessive sweating, such as during exercise or hot weather
- Fluid loss due to diarrhea or vomiting
- Fever, which increases fluid evaporation from the body
- Excessive sun exposure, which accelerates water loss from the skin
A combination of these factors can cause the skin to lose moisture more quickly and appear dull.
How to Prevent Skin Dehydration

Preventing dehydrated skin is not just about skincare. It also involves daily habits.
1. Maintain Internal Hydration
Drinking enough water every day is essential. Generally, about 2 liters per day is recommended, with higher intake needed during hot weather or intense physical activity.
Limit alcohol consumption, as it has a diuretic effect and can accelerate fluid loss.
2. Protect the Skin Barrier
Bathing habits also affect skin hydration:
- Avoid bathing or soaking for too long
- Use lukewarm water instead of hot water
- Dry the body by gently patting the skin, not rubbing
3. Choose Gentle Cleansers
Use facial and body cleansers that are gentle, non-alkaline, and have a pH close to the skin’s natural pH. Harsh cleansers can damage the skin barrier and worsen dehydration.
4. Use Moisturizer Regularly
Moisturizers play an important role in locking in hydration. Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing, while the skin is still slightly damp, to help absorb moisture more effectively.
5. Pay Attention to Clothing Choices
Avoid overly tight clothing or rough, synthetic fabrics such as wool. Choose soft, breathable materials to reduce irritation and prevent excessive moisture loss from the skin.
References
Medical News Today. Accessed in 2025. Is My Skin Dehydrated?
Paula Choice. Accessed in 2025. How to Identify and Treat Dehydrated Skin.







Leave feedback about this