For people with diabetes, keeping blood sugar levels stable isn’t just a routine. It’s an essential part of daily life.
Blood sugar (or blood glucose) refers to the amount of sugar circulating in your bloodstream. When levels become too high or too low, it can cause serious health issues.
In diabetes, the body’s ability to produce or use insulin doesn’t function properly. As a result, glucose can’t enter the cells to be used for energy.
Left unmanaged, this condition can lead to long-term complications such as nerve damage, kidney problems, heart disease, and vision disorders.
Why Is Blood Sugar Management Important?
Uncontrolled blood glucose levels can trigger a range of health problems. The good news is that with proper management, including a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and prescribed medications, diabetes can be effectively controlled.
You can still lead an active, productive life.
Daily Tips for Managing Diabetes
1. Take Medications as Prescribed
Always take your diabetes medications exactly as directed by your doctor, even when your blood sugar levels are within the normal range.
These medications help your body regulate glucose, and skipping doses can lead to spikes or dangerous drops in blood sugar.
Some side effects, like nausea or diarrhea, may occur in the beginning, but they usually improve over time.
2. Eat a Balanced Diet
Nutritious food is the foundation of diabetes management. Focus on eating:
- Leafy and non-starchy vegetables
- Low-sugar fruits
- Lean protein sources
- High-fiber complex carbohydrates
Also, please pay attention to meal timing and portion sizes, especially when it comes to carbs.
Blood sugar tends to spike after large or sugary meals, so it’s essential to monitor your levels regularly, especially when trying new foods.
3. Stay Active
Physical activity helps your body use insulin more efficiently. It also supports a healthy weight, lowers blood pressure, and boosts energy.
You don’t have to start with a marathon; a brisk 20–30 minute walk each day is enough. Even light activities like gardening or climbing stairs can make a difference.
Blood Sugar Target
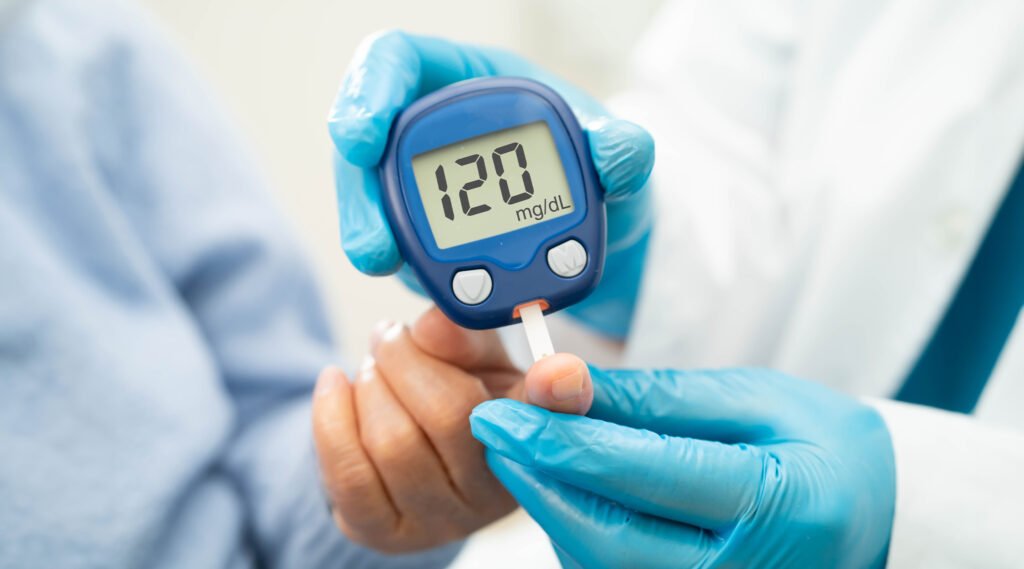
Blood sugar goals may vary depending on your age and any other health conditions, but general targets include:
- Before meals: 80–130 mg/dL
- Two hours after meals: Less than 180 mg/dL
Talk to your doctor to determine the most appropriate personal targets for you.
When Should You Check Your Blood Sugar?
How often you need to monitor your blood sugar depends on the type of diabetes you have, your treatment plan, and your daily routine. Recommended times include:
- After waking up (fasting)
- Before and 2 hours after meals
- Before exercising
- Before going to bed
If you’re using insulin, checking before meals can help you determine the correct dose.
How Does the Body Process Sugar?
When we eat foods that contain carbohydrates, the body breaks them down into glucose, which enters the bloodstream.
The pancreas then releases insulin, a hormone that helps glucose move into the cells for energy.
In people with diabetes, this process is disrupted either because the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin or because the cells don’t respond appropriately to it. That’s why blood sugar levels can remain high, even if you’re eating “just enough.”
Managing blood sugar is a long-term investment in your health.
With consistency and support from healthcare professionals, you can take control of your diabetes and live a healthy, active, and complication-free life.
References
CDC. Accessed in 2025. Manage Blood Sugar.
Compass Cross Benefits. Accessed in 2025. Managing Blood Glucose: What You Need to Know.
Healthline. Accessed in 2025. What You Should Know About Managing Glucose Levels.












Leave feedback about this